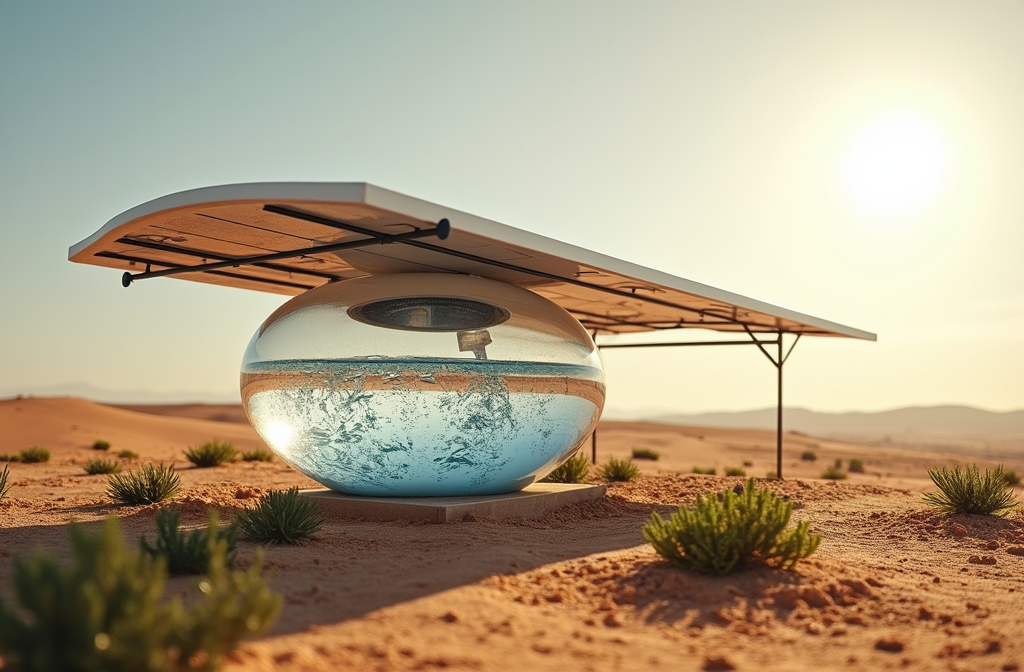
Freshwater scarcity is a growing global crisis, affecting over 2.2 billion people. From arid deserts to remote island territories, the need for sustainable, decentralized water solutions is more pressing than ever. Traditional water sourcing methods often require vast infrastructure, high energy consumption, and regular maintenance—barriers that make them unfeasible for many communities. However, a groundbreaking new technology may provide the answer: a passive solar-driven atmospheric water extraction (SAWE) system that continuously harvests water from the air, even in low-humidity environments.
This cutting-edge SAWE system operates entirely on sunlight, extracting moisture from the atmosphere to generate freshwater for drinking and irrigation. Unlike previous designs that require manual operation or complex moving parts, this system is completely passive, making it an ideal solution for off-grid and water-scarce regions.
How the Solar-Powered Atmospheric Water Extraction System Works At the heart of this innovation is a specially designed three-dimensional structure optimized for continuous moisture capture and water production. The system consists of microchannel-infused mass transport bridges (MTBs) that facilitate the spontaneous movement of water and energy, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
- Atmospheric Water Capture – A liquid sorbent (lithium chloride solution) absorbs moisture from the air, even in environments with relative humidity as low as 40%.
- Solar-Powered Water Release – Sunlight heats the system’s absorber, converting the captured moisture into vapor.
- Condensation and Collection – The vapor cools and condenses into freshwater, which is then collected for use.
- Continuous Cycle – A built-in equilibrium system ensures that the liquid sorbent is continuously replenished, enabling non-stop water production.
This innovative mechanism allows the SAWE system to generate up to 3 liters of water per square meter per day in humid climates, and it remains functional even in dry conditions.
Real-World Performance: Field Testing in Saudi Arabia To validate its efficiency, researchers deployed a scaled-up version of the SAWE system in Thuwal, Saudi Arabia, for a 35-day field test spanning both summer and fall seasons. The results were impressive:
- Summer Performance: The system produced between 2.0–3.0 liters per square meter per day.
- Fall Performance: Water generation ranged from 1.0–2.8 liters per square meter per day.
- No Maintenance Required: The system operated continuously without the need for intervention, demonstrating its self-sufficiency.
A Game-Changer for Off-Grid Irrigation Beyond providing drinking water, this SAWE system has the potential to revolutionize agriculture in arid regions. Researchers successfully used the harvested water to irrigate Chinese cabbage plants, proving its viability for sustainable farming. A fully autonomous drip irrigation setup was tested, ensuring minimal water loss while maintaining optimal soil moisture levels.
Key takeaways for agriculture:
- The system enables off-grid irrigation without dependence on traditional water sources.
- It supports plant growth comparable to conventional water supplies.
- It has the potential to sustain desert agriculture and reforestation projects.
Why This Technology Matters The global potential for solar-driven atmospheric water extraction is enormous. With over six times the volume of Earth’s river water stored in the atmosphere at any given time, harnessing this resource could alleviate water shortages in vulnerable regions. Key advantages of this system include:
✔ Zero Energy Costs – Fully solar-powered operation eliminates the need for external power sources.
✔ Scalability – The modular design allows easy expansion to meet higher water demands.
✔ Minimal Environmental Impact – No groundwater depletion or large infrastructure required.
✔ Affordability – Simple, cost-effective materials make it an accessible solution for rural communities.
Final Thoughts: A Step Towards a Water-Secure Future This revolutionary SAWE system could play a crucial role in addressing the global water crisis. By leveraging sunlight to continuously extract water from the air, it provides a sustainable and scalable solution for both drinking water and agriculture. Whether in isolated villages, deserts, or urban environments with unreliable water access, this technology paves the way for a more water-secure world.
As climate change and population growth continue to strain water resources, innovations like this will be vital in shaping a sustainable future. With further research and scaling, solar-powered atmospheric water extraction could soon become a mainstream solution, offering hope to millions worldwide.
Article derived from: Yang, K., Pan, T., Ferhat, N. et al. A solar-driven atmospheric water extractor for off-grid freshwater generation and irrigation. Nat Commun 15, 6260 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-50715-0
Check out the cool NewsWade YouTube video about this article!