What Happened?
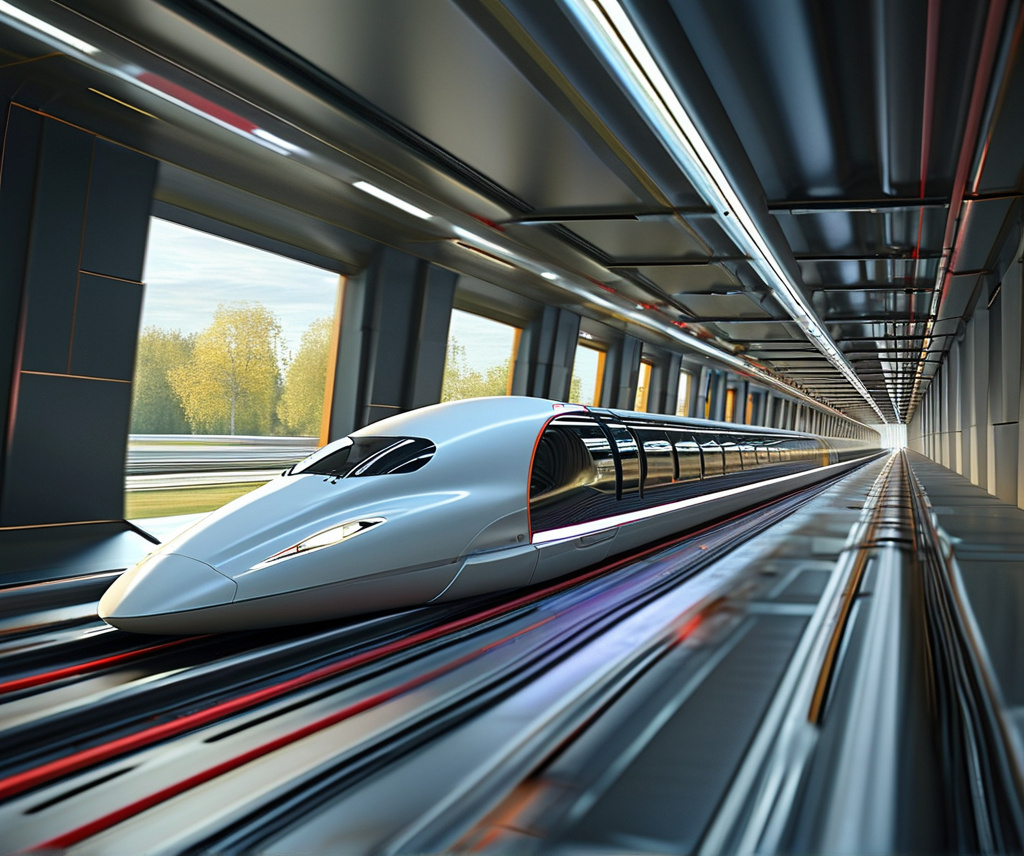
- Event: Hardt Hyperloop, a company developing hyperloop technology, successfully conducted its first test in the Netherlands.
- Details: The test took place at the European Hyperloop Center (EHC) in Veendam, on a 420-meter test track. Their hyperloop vehicle demonstrated its core technologies, such as magnetic levitation (lifting off the ground), propulsion (movement), and guidance systems.
- Significance: This is a huge milestone in making hyperloop transportation a reality, setting the stage for future tests at higher speeds.
Why is this Important?
- Revolutionizing Transport: Hyperloop could transform global travel by drastically reducing travel times. Imagine traveling between cities in minutes rather than hours. For example, trips that currently take 3-4 hours could be cut down to under an hour.
- Energy Efficiency: The hyperloop is designed to use less energy than traditional transportation, which can make it a more environmentally friendly option. The magnetic levitation allows the vehicle to “float,” reducing friction, while moving in a low-pressure tube minimizes air resistance.
- Innovative Design: Unlike trains or airplanes, hyperloop vehicles don’t rely on fossil fuels for propulsion, making them a promising technology for reducing carbon emissions.
Who Was Involved?
- Company: Hardt Hyperloop, a European company leading the hyperloop technology race.
- Facility: The European Hyperloop Center in Veendam, Netherlands, is the testing site. It’s the longest hyperloop test track in Europe at 420 meters and was designed specifically for advancing hyperloop research.
How Does it Work?
- Technology Basics:
- Magnetic Levitation: This technology makes the hyperloop vehicle float above the track, eliminating physical contact and friction.
- Propulsion System: Using electric motors, the vehicle is pushed forward through the tube. The lack of air resistance and the reduced pressure in the tube allows the vehicle to reach much higher speeds than conventional trains.
- Guidance: The track has systems to keep the vehicle aligned and prevent it from veering off.
- Speeds: Although this first test only reached 30 km/h (19 mph), future tests aim to push speeds over 700 km/h (430 mph).
How Will It Benefit Humanity?
- Faster Commutes: Hyperloop systems could make traveling between cities incredibly fast, transforming business, tourism, and daily commuting.
- Environmentally Friendly: Unlike planes and cars, the hyperloop can operate using renewable energy, potentially eliminating carbon emissions. This could help combat climate change.
- Efficiency in Goods Transport: Hyperloop systems could also be used to transport freight, making shipping more efficient and less reliant on fossil fuels.
- Cost Saving: With less reliance on fuel and fewer moving parts compared to planes and trains, maintenance costs for hyperloop systems may be lower, potentially making it a cheaper alternative in the long run.
When Will It Be Available?
- Next Steps: Hardt Hyperloop plans full-speed tests later this year, reaching up to 100 km/h.
- Long-term Vision: It will take several more years of research and testing before hyperloop systems are ready for public use. The technology is still in its experimental phase, and large-scale commercial use may happen sometime in the next decade.
Article derived from: Jowitt, T. (2024, September 11). Successful hyperloop test completed in Holland. Silicon UK. https://www.silicon.co.uk/e-innovation/research/successful-hyperloop-test-completed-in-holland-579299
Disclaimer: This content was simplified and condensed using AI technology to enhance readability and brevity.