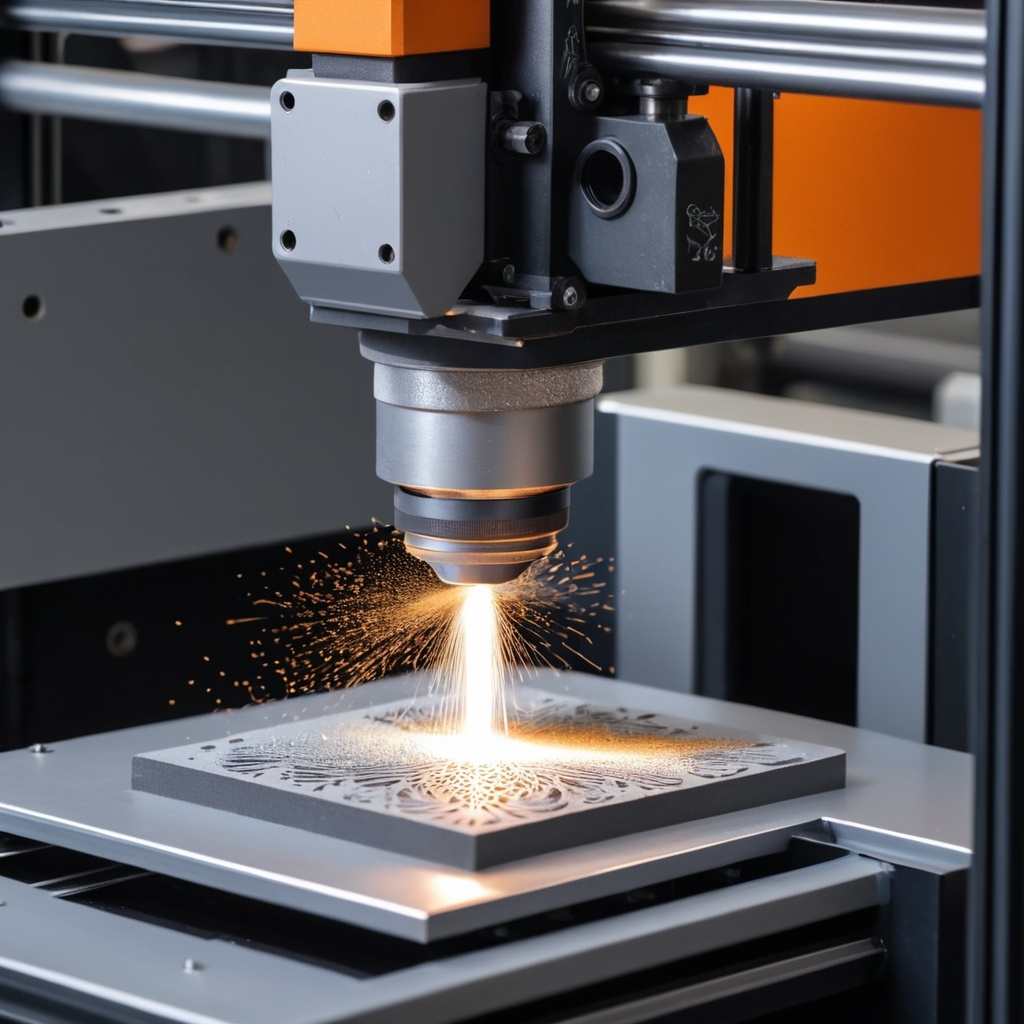
Binder jetting is like a super-advanced printer that uses metal powder instead of ink. It squirts a glue-like binder onto the powder to stick it together layer by layer, creating solid metal objects. Think of it as a way to make cool stuff without needing to carve or mold materials!
What happened?
- Emergence of Binder Jetting Technology: Binder jetting has recently gained attention as an innovative 3D printing method. Unlike traditional methods that carve or mold materials, binder jetting bonds metal powders together using a liquid binder. This process enables the production of intricate designs that would be difficult or expensive to create using conventional techniques.
Why?
- Limitations of Traditional Manufacturing: Traditional manufacturing methods, such as machining or injection molding, can be time-consuming, costly, and wasteful. They often require extensive setup and tooling, which increases lead times and production costs.
- Demand for Customization: Many industries, such as aerospace and healthcare, require customized parts to meet specific needs. Binder jetting offers a flexible solution that can quickly adapt to changing requirements without significant retooling.
Who?
- Key Players: Companies like Desktop Metal, ExOne, and HP are leading the way in developing and commercializing binder jetting technology. These firms focus on industries that demand high precision and efficiency in manufacturing.
- Target Industries: Industries such as automotive (for producing lightweight components), aerospace (for complex engine parts), and healthcare (for custom implants and devices) are major beneficiaries of this technology.
How it works:
- Layering Process:
- Powder Spreading: A layer of fine metal powder is evenly spread across a build platform.
- Binder Application: A print head moves over the powder, depositing a liquid binder in specific areas according to the digital design. This binds the powder particles together.
- Layering: The process is repeated, adding layers of powder and binder until the object is complete.
- Post-Processing: Once printed, the object is removed from the build chamber. It usually undergoes sintering, where it’s heated to a temperature that causes the metal particles to fuse together, resulting in a strong, solid piece.
How it will benefit humanity:
- Increased Efficiency: Binder jetting allows for faster production cycles compared to traditional manufacturing. This speed can lead to shorter lead times for products, enabling companies to respond quickly to market demands.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: By minimizing material waste and reducing setup times, binder jetting can lower manufacturing costs, making advanced technology more accessible to smaller companies and startups.
- Design Freedom: The ability to create complex geometries can lead to innovations in product design, improving functionality and performance while reducing weight.
When it will be available:
- Current Use: Binder jetting technology is already being utilized by various manufacturers and is seeing increasing adoption in multiple sectors.
- Future Developments: Ongoing research and development are expected to enhance the capabilities of binder jetting, making it even more efficient and versatile. As technology advances, it is likely to become more mainstream in manufacturing practices over the next few years.
Metal, D. (n.d.). Why binder jetting? Desktop Metal. https://www.desktopmetal.com/resources/why-binder-jetting-1
Disclaimer: This content was simplified and condensed using AI technology to enhance readability and brevity.