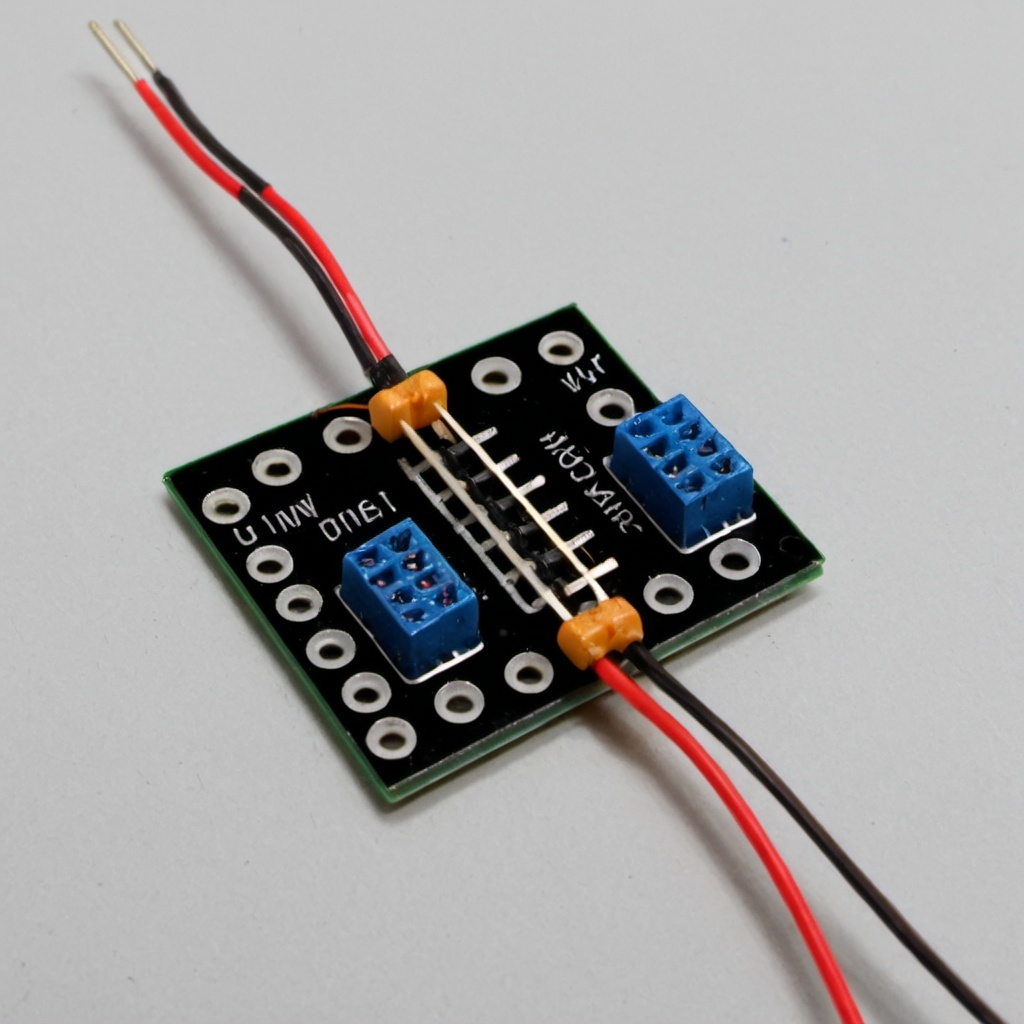
Imagine you have a very basic setup of wires and small devices on a table, much like a simple DIY electronics project. A scientist named Sam Dillavou has created such a setup that can perform basic data sorting tasks, similar to how our computers work today. But here’s the interesting part: instead of using the complex and power-hungry parts found in regular computers, this setup uses very simple and energy-efficient components called resistors.
How It Works
- Analog vs. Digital: Regular computers process information using digital signals (1s and 0s). Sam’s setup uses analog signals, which can have a range of values. Think of it like the difference between a light switch (digital – on/off) and a dimmer switch (analog – various levels of brightness).
- Learning from Feedback: The resistors in this setup can adjust themselves based on the information they receive, somewhat like how our brains adjust to new information. This method is inspired by how neurons in our brains work.
- Energy Efficiency: Because it uses analog signals and simple components, this setup has the potential to be much more energy-efficient than traditional digital computers. However, it’s still in the early stages, and the energy savings are not yet fully realized.
Benefits to Humanity
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Computers, especially those used for heavy processing tasks like artificial intelligence (AI), consume a lot of electricity. A more energy-efficient computer could significantly reduce this power usage, leading to lower electricity bills and less strain on power grids.
- Environmental Impact: Lower energy consumption means fewer greenhouse gas emissions from power plants, contributing to the fight against climate change.
- Cost Savings: Cheaper and more efficient computing could make advanced technologies more accessible, benefiting industries and individuals alike.
In summary, Sam Dillavou’s simple circuit represents an innovative step towards creating more energy-efficient computers. While it is still a prototype, its potential to save energy and reduce environmental impact makes it a promising development for the future.
Disclaimer: This content was simplified and condensed using AI technology to enhance readability and brevity.
Article derived from: Chen, S. (2024, July 16). How a simple circuit could offer an alternative to energy-intensive GPUs. MIT Technology Review. https://www.technologyreview.com/2024/06/05/1093250/how-a-simple-circuit-could-offer-an-alternative-to-energy-intensive-gpus/