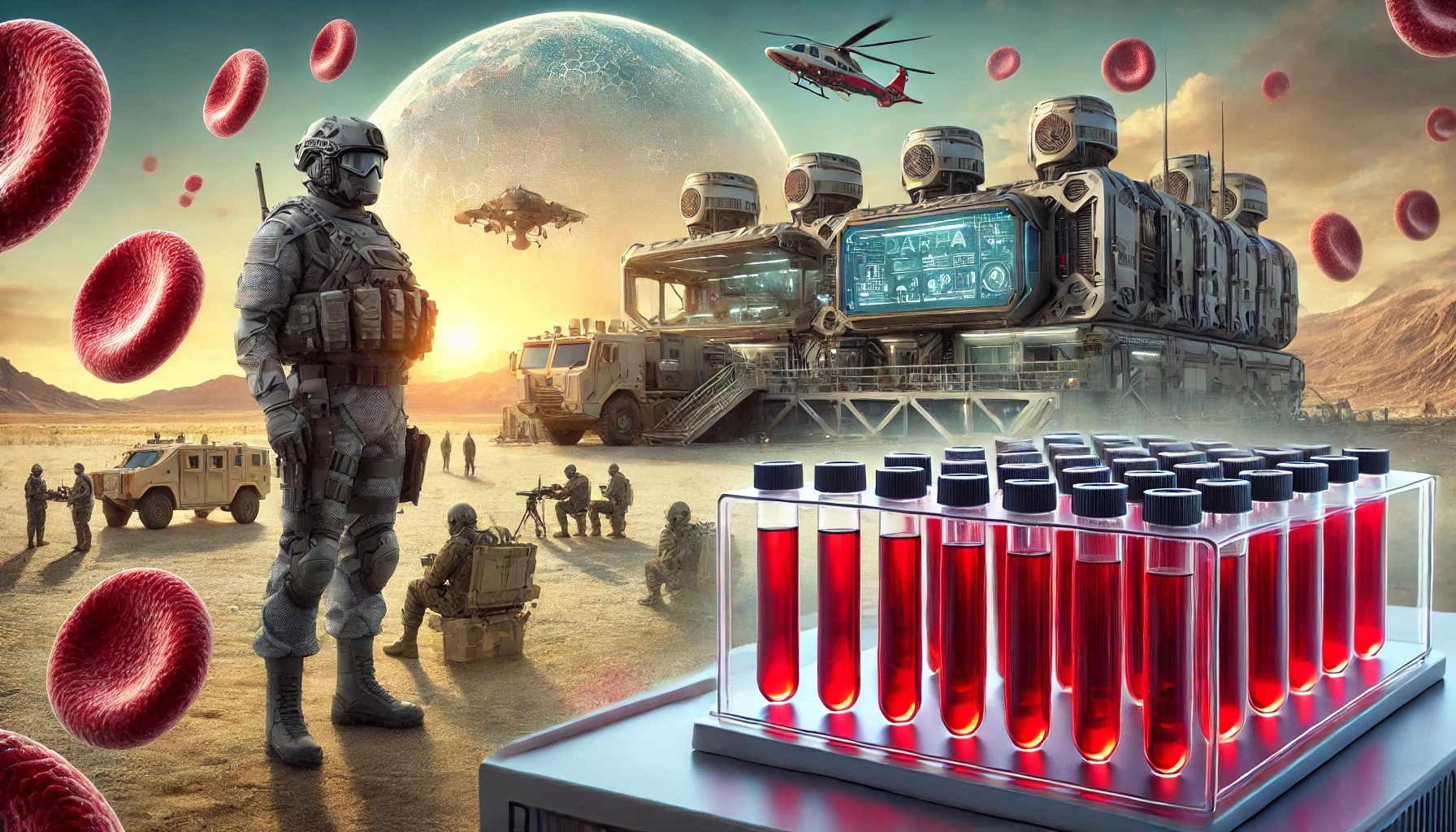
Imagine a future where soldiers are protected from extreme environmental conditions by enhancements within their own blood cells. DARPA’s RBC Factory project is turning this futuristic vision into reality by bioengineering red blood cells (RBCs) to act as miniaturized protective agents. These modified cells could provide warfighters with adaptable, internal protection against threats such as extreme heat, cold, radiation, or chemical exposure—without the need for bulky equipment or continuous medication.
The Science Behind RBC-Factory
The human body’s red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen to tissues. DARPA’s project aims to add extra capabilities to these cells by inserting peptides, proteins, or pigments into their membranes. The process involves temporary, reversible modifications to create a defense mechanism that lasts as long as the lifespan of the red blood cells—about 120 days.
This approach could allow soldiers to withstand harsh environments or recover faster from injuries, leveraging the body’s natural systems to provide built-in resilience. DARPA envisions applications ranging from increased tolerance to high altitudes and extreme temperatures to enhanced protection against biological and chemical threats.
Potential Benefits for Soldiers and Civilians
The RBC Factory project could revolutionize how soldiers operate in extreme environments. Currently, warfighters often carry heavy protective gear and rely on medications to mitigate environmental risks. With engineered blood cells, the need for external equipment could be significantly reduced, improving mobility and endurance.
But the potential doesn’t stop with military applications. Civilian healthcare could benefit from these innovations as well. Imagine treatments that could protect vulnerable populations from environmental hazards or boost recovery from illnesses by enhancing the body’s natural defenses.
Ethical Considerations and Future Implications
While the science is groundbreaking, it comes with ethical concerns. Modifying human biology, even temporarily, raises questions about long-term impacts and unintended consequences. DARPA has committed to addressing these concerns through strict regulatory compliance and ethical oversight.
If successful, the RBC Factory could redefine human adaptability. The concept of engineered resilience through blood cells may eventually pave the way for broader applications, from healthcare innovations to space exploration, where humans will need to endure extreme conditions.
Why This Matters for Humanity
DARPA’s RBC Factory is more than just a military advancement. It’s a glimpse into the future of human augmentation—where our biology can be tuned to withstand harsh environments, protect us from unseen dangers, and optimize our performance.
Whether you’re interested in cutting-edge science or wondering about the future of human adaptability, this project signals a bold step forward in merging biology with technology.
Article derived from: Protecting warfighters in Extreme environments | DARPA. (n.d.). https://www.darpa.mil/news/2024/rbc-factory
Check out the cool NewsWade YouTube video about this article!